Research Article - Volume 3 - Issue 3
Anatomical classification of catterpillar hump of RHA and its surgical importance (nagpur classification)
Prashant Rahate1*; Zoeb Haidar2; Akshay Bangde3; Amol Belsare3; Vipul Golchha3; Kunal Yadav3; Nachiket Rahate3
1Consultant Surgeon, Director Seven Star Hospital, Nagpur, India.
2Fellow in Minimal Access Surgery, Seven Star Hospital, Nagpur, India.
3Final year, JNMC, DMIMSDU, Sawangi (Meghe), Wardha, India.
Received Date : Mar 24, 2023
Accepted Date : May 05, 2023
Published Date: May 10, 2023
Copyright:© Prashant Rahate* 2023
*Corresponding Author : Prashant V. Rahate. M.S, CMD, Seven Star Hospital, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India.
Email: prashantrahate84@yahoo.com
DOI: Doi.org/10.55920/2771-019X/1430
Abstract
Background: Ligation of cystic artery is important surgical step involving gallbladder and hepatobiliary surgery. Right hepatic artery may come very close to gallbladder & cystic duct and CHD in the form of “Caterpillar hump or Moynihan hump’’. Such hump has variations in position and depending on hump type, cystic artery anatomy is defined. In this situation right hepatic artery is liable to be mistakenly identified as cystic artery and it will be ligated prior to Cholecystectomy leading to right functional lobe of liver goes for necrosis. By defining types, increasing surgeon’s awareness, surgical complications will be reduced
Materials and Methods: 600 videos of laparoscopic surgery of gall bladder and CBD exploration were retrospectively reviewed for presence of caterpillar hump in RHA in Rahate Surgical hospital and Seven-star Hospital, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India from 2012 to 2021 April. Lot of literature was reviewed. Type of hump and its anatomical relations and difficulty level of laparoscopic surgery because of hump was assessed
Result: Caterpillar hump was present in 21 cases (3.5%) in present study. We found lot of anatomical variations of hump, and judged the level of difficulty of laparoscopic cholecystectomy depending on type of caterpillar hump. We propose a simple classification of type of caterpillar hump depending on observations
Conclusion: knowing the vascular anatomy and likelihood of complications should be known to all surgeons. So that the surgeons are able to identify this arterial variation during their cholecystectomy surgeries. If this caterpillar hump of right hepatic artery is present, the surgeons should locate the origin of cystic artery to avoid any unnecessary confusion between cystic artery and right hepatic artery for preventing unnecessary damage to the right hepatic artery. In an attempt to classify caterpillar hump, we can define, predict position of cystic artery type and variation, thereby helping in preventing vascular complications during laparoscopic cholecystectomy and CBD exploration
Keywords: Caterpillar hump, Moynihan hump, right hepatic artery injury, Cystic artery, Cholecystectomy., Laparoscopic cholecystectomy, vascular injury during lap. Cholecystectomy, Difficult callots anatomy.
Introduction
Good optics and infrared imaging and safe energy sources added recently in armamentarium of surgeons has increased safety of laparoscopic cholecystectomy and CBD exploration. In spite of advancement and improvement in techniques, certain anatomical variations spring surprises, and may lead to surgical complications -biliary and vascular. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy makes it mandatory to have a thorough knowledge of normal anatomy and variations in this region to reduce the likelihood of uncontrolled intraoperative bleeding, iatrogenic extrahepatic biliary injury and conversion to open cholecystectomy [1]. Incidence of conversion to open surgery because of vascular injury is 0-1.9% and mortality is 0.02 % [2]. The right hepatic artery after its origin from hepatic artery proper crosses anterior to the portal vein and then passes behind the common hepatic duct to enter the Calot’s triangle (bounded by cystic duct, common hepatic duct and lower edge of the liver). As it approaches the cystic duct, it gives off the cystic artery and then turns upwards, behind (and between) the right hepatic and the cystic duct to the right lobe of the liver (figure 1, figure 2). The cystic artery normally arising from the right hepatic within the triangle, passes in the triangle toward the neck of gall bladder where it typically divides into two branches one of which runs on the attached surface of the gall bladder and the other on its peritoneal surface [3]. Tortuous right hepatic artery, running with upward and downward course producing hump is rarely described anomaly [4]. This tortuosity of the right hepatic artery is called caterpillar hump or Moynihan’s hump [5]. Both inside and outside the Calot’s triangle, the right hepatic often makes a characteristic caterpillar like loop, convexity of which points downward, upward, to the right or to the left. In cholecystectomy, such tortuosity of the right hepatic is extremely vulnerable, for the cystic artery may arise from the distal or the proximal end of the loop, in the latter instance crossing it.
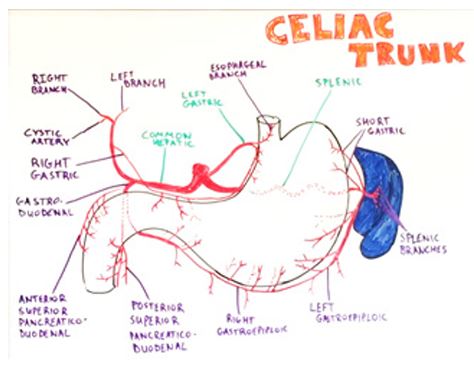
Figure 1: Course and branches of celiac trunk (schematic).
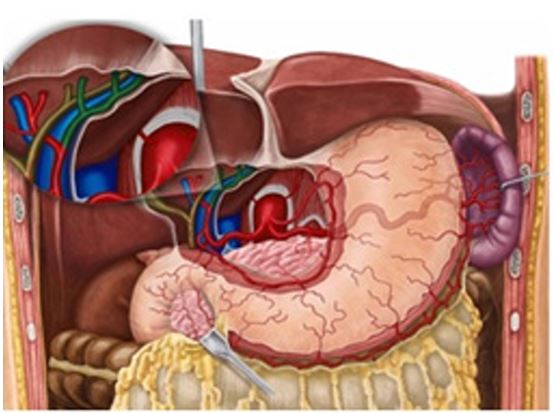
Figure 2: Anatomical relations of CHA.
reference to the cystic duct.
(A) More nearer the hump to CD shorter will be CA.
(B) The hump can be anterior or posterior to CHD.
(C) Hump can be single loop or double loop
(D) Cystic artery can be single or double (anterior and posterior)
(E) A bend in the course of the right hepatic artery throwing it into the caterpillar hump invites injury unless it is carefully dissected free.12 This variant of right hepatic artery invariably leads to abnormalities of cystic artery formation which can result in its injury during surgical procedures Types of caterpillar hump -Since cystic duct is taken as reference, depending on the anatomical relationship of caterpillar hump to cystic duct classification of hump is done.
1)Supracystic: The hump is either anterior or posterior to CHD, superior to the cystic duct, nearer to hilum of liver. Here the cystic artery is long, originating from inferior part of loop hump. Due to long cystic artery, and hump remaining away from surgical dissection, mishaps are less during surgery
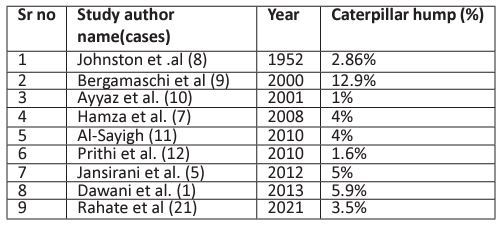
2) Paracystic: The hump is around the confluence of cystic artery and CHD. Here the hump usually gives off two branches, anterior cystic artery and post cystic artery. since the hump is very close to cystic duct, the cystic arteries are very short. the hump (RHA) is mistaken for CA and high chances of vascular catastrophe during surgery.
3)Infracystic: The hump is below the confluence towards duodenum, here again the CA is long, single, originating from ascending part of hump. surgical mishaps are less for obvious reason. Depending on other anatomical details caterpillar hump can be classified further as follows:
A) Anterior / posterior (loop position in relation to CHD / CBD)
B) Single hump / double hump (depending on number of hump) [8] C)single cystic artery / double cystic artery(Figure 3) .
Surgical significance
Variant of right hepatic artery invariably leads to abnormalities of cystic artery formation which can result in its injury during surgical procedures Since the cystic artery arising from the loop is typically short, it may get easily avulsed from the hepatic artery, if excessive traction is applied to the gall bladder producing brisk bleeding [24].
Sometimes tortuous right hepatic artery does not give a single cystic artery but supplies the gall bladder with several small twigs. The right hepatic artery is injured while securing them. Injury to right hepatic artery can be fatal in presence of impaired liver function and associated biliary injury [24-26]. It is usually the right hepatic artery that is in danger during this surgery and must be located before ligating the cystic artery [5]. Because numerous variations in origin and branching pattern of right hepatic artery have been reported [27].
The Hump lies in close proximity to the gall bladder and cystic duct and so it may be mistaken to be cystic artery and inadvertently ligated during surgical procedures like cholecystectomy and liver transplantation [5,7,11,13]. So caterpillar hump should be suspected when an unusually large ‘cystic artery’ is seen through the laparoscope [5,13]. It must be emphasized that an artery resembling the cystic artery in its course and paralleling the cystic duct is not necessarily the cystic artery but may be right hepatic artery and the calibre of vessels to be
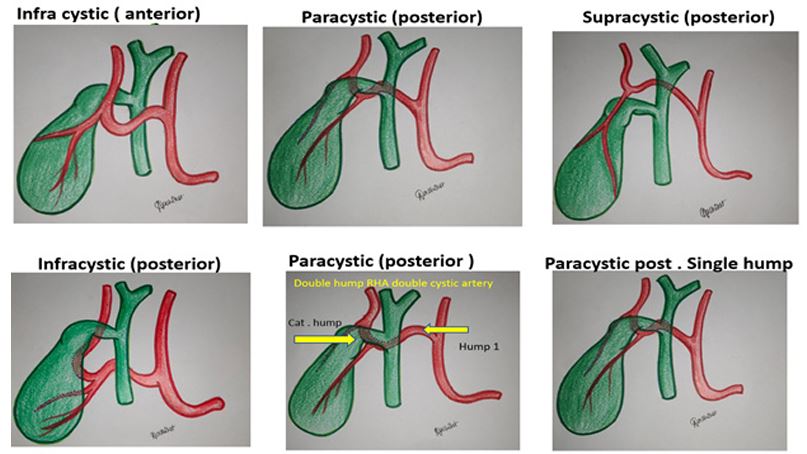
Figure 3: Schematic diagrams of types of caterpillar hump (Moynihan’s).
divided is not a reliable index of whether it is cystic artery or right hepatic artery. Therefore, it is essential to visualize right hepatic artery above and below the origin of cystic branch [28,29].
Accurate knowledge of cystic artery and right hepatic artery anatomy and its variations can reduce the likelihood of uncontrolled intraoperative bleeding, an important cause of iatrogenic extra hepatic biliary injury and conversion to open cholecystectomy [29-31]. The incidence of conversion to open surgery due to vascular injury is reported to be 0-1.9% and its mortality 0.02% [29], hence these variations should stay in surgical conscience to prevent procedure related morbidity. We aim to present the variations in cystic artery seen in laparoscopic cholecystectomy in our patient population.
Material and Method
600 videos of laparoscopic surgery of gall bladder and CBD exploration were retrospectively reviewed for presence of caterpillar hump in RHA in Rahate Surgical Hospital and Seven Star Hospital, Nagpur, India from 2012 to 2021 April Lot of literature reviewed. Type of hump and its anatomical relations and difficulty level of laparoscopic surgery because of hump was assessed. 21 cases were found to have caterpillar hump. various types of humps as per relation with cystic duct defined
as follows:
- Supracystic hump (position of hump superior to cystic duct)
- Paracystic (position of hump at same level of cystic duct)
- Infracystic (position of hump below the cystic duct)
Depending on anterior or posterior position of hump in relation to CBD and CHD, hump was further classified as follows:
1) supracystic -a) anterior
b) posterior
2) Paracystic- a) anterior
b) posterior
3) Infracystic a) anterior
b) posterior
Further cystic duct number and position defined. A specific relationship between cystic artery number and type of hump was noted as follows
- Supracystic and Infracystic hump- only one cystic artery which divides in to two anterior and posterior cystic arteries. Length of cystic arteries is long
- Paracystic hump - Anterior and posterior cystic arteries originate separately, that means there are two cystic arteries. Both cystic arteries are short in length. Hence, chances of injuring RHA is high in Paracystic caterpillar hump
Results
Table 1: Incidence percentage of types of caterpillar hump seen in present study (this is a single centre study, we need more multicentric studies by surgeons and anatomist to know the incidence of caterpillar hump, its various types surgical corelation).
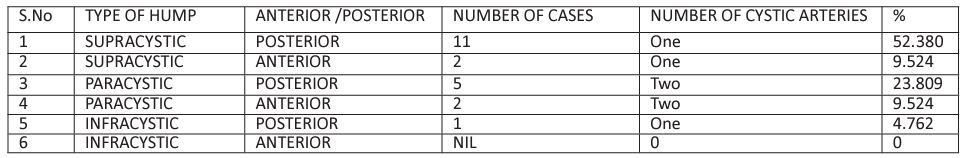
Table 2: Incidence of Caterpillar Hump of RHA in various studies.
Discussion
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy was initially associated with a significant increase in morbidity due to increased incidence of biliary injuries and haemorrhages. This was perhaps due to a lack of knowledge of the ‘laparoscopic anatomy’, two dimensional ‘laparoscopic view’ and the dissection with long instruments without tactile feedback [29,32]. Misinterpretation of normal anatomy and anatomical variations contributed to major postoperative complications33. Conventional textbook description of the regional blood supply did not seem adequate in laparoscopic view [34].
With the availability of good optics supported by infrared imaging and improvement in energy sources for dissection, callots anatomy became increasingly clear and safe. smallest of anatomical details and deviations were recorded.
Similarly, various classifications of cystic artery were proposed in the literature. Ignjatovic et al [35] described 3 types of cystic artery; Type 1 was described as single artery in Calot’s triangle; Type 2 more than one artery in Calot’s triangle and Type 3 no artery in Calot’s triangle. Balija et al [36] described two groups; in group 1, cystic artery, either single or double, was present in the triangle and in group 2 no artery was seen in the triangle on laparoscopic visualization. He did not comment on cases where vessels were seen both inside and outside the Calot’s triangle. Ding et al [29] in their classification describe 3 groups; Group I have artery/arteries in the triangle, Group II has the artery outside the triangle and Group III has compound arteries, both inside and outside the triangle. They also described these arterial variations according to their origin
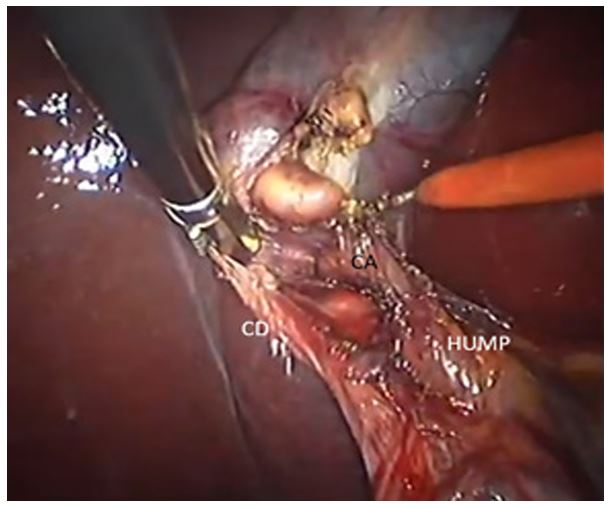
Figure 4: Supracystic caterpillar hump
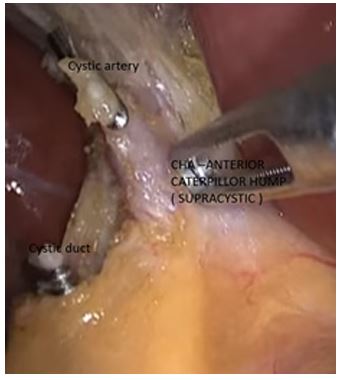
Figure 5: Anterior supracystic hump.
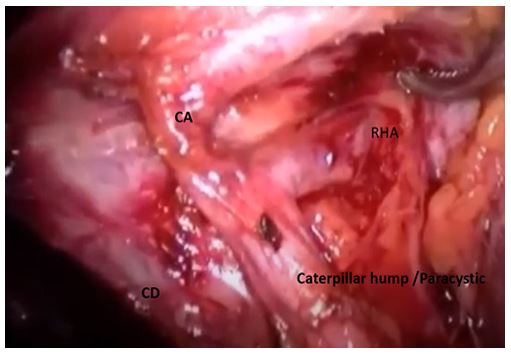
Figure 6; Infracystic hump- because of cephalad traction to infundibulum, hump appears Paracystic, if traction is released, hump descends to Infracystic .
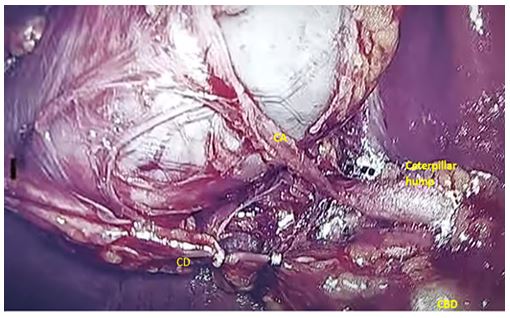
Figure 7: Supracystic anterior caterpillar hump with long cystic artery
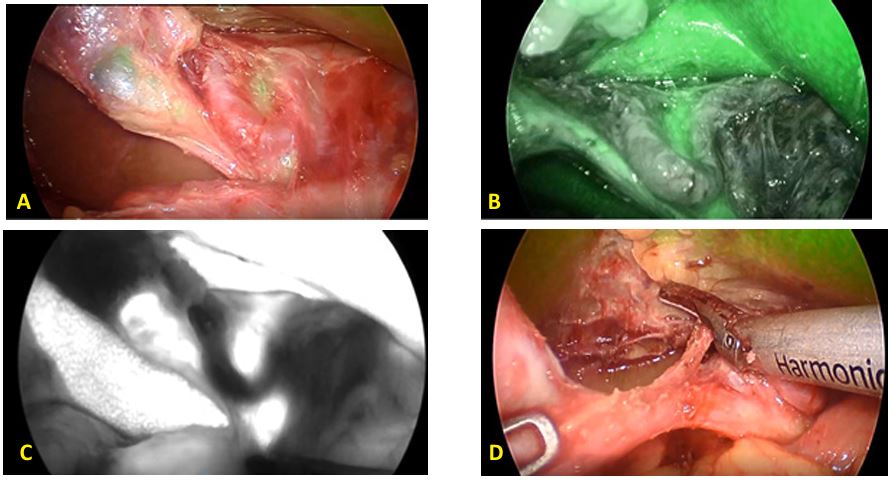
Figure 8: Para cystic caterpillar hump (A) CH with ICG shadow of CHD IN loop, (B)ICG view of callots triangle, (C) contrast view showing CHA caterpillar hump (D) short CA
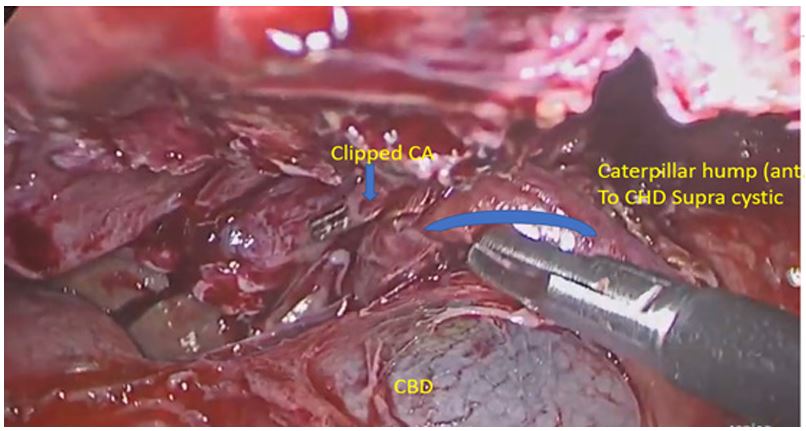
Figure 9: Anterior supracystic caterpillar hump going medially and posteriorly hugging CHD giving a short anterior CA and long posterior CA (double cystic artery).
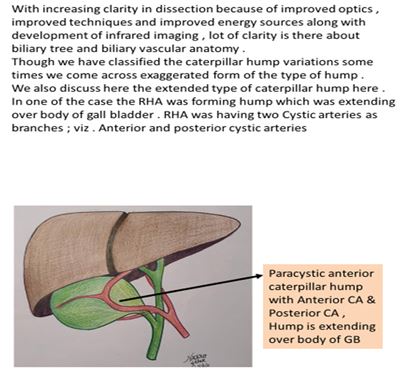
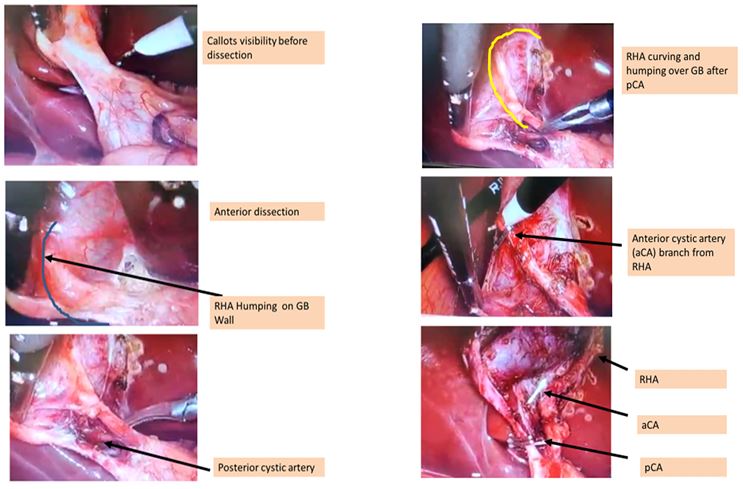
The commonest variation was that of double arteries in Calot’s triangle in 11.8% patients [1]. This pattern has been seen in 15 to 25 % of many published series [36,37], but Suzuki has described this pattern in only 2.45 % of his patients 10. At this point we can say that multiple cystic arteries in callots are due to Paracystic caterpillar hump which previous workers failed to notice that time.
Balija describes a cystic artery originating from aberrant right hepatic artery entering the Calot’s triangle from behind the portal vein and paralleling the cystic duct, occasionally forming a prominence in this area (caterpillar hump) This artery yields multiple small branches, rather than a single branch, but within the triangle [35].
Conclusion
With increasing incidence of gall bladder and ductal disease, knowing the vascular anatomy and likelihood of complications should be known to all surgeons. Ductal anatomy had been extensively studied and documented. Vascular anatomy has been little neglected, this is an attempt to make surgeons aware of callots triangle vascular anatomy. So that the surgeons are able to identify this arterial variation during their cholecystectomy surgeries. Potentially precarious RHA in caterpillar hump variation has been classified and extensively studied for variations of positions and cystic artery anomalies. The classification has been named as NAGPUR CLASSIFICATION after the city of origin of the author. If this caterpillar hump of right hepatic artery is present, the surgeons should locate the origin of cystic artery to avoid any unnecessary confusion between cystic artery and right hepatic artery for preventing unnecessary damage to the right hepatic artery. In an attempt to classify caterpillar hump, we can define, predict position of cystic artery type and variation, thereby helping in preventing vascular complications during laparoscopic cholecystectomy and CBD exploration. This is single centre observation involving a single surgical team. This topic needs multi centre analysis with surgeons and anatomist.
References
- Zubair M, Habib L, Mirza MR, et al. Anatomical variations of cystic artery: telescopic facts. Med J Malaysia. 2012; 67(October (5)): 494-496.
- Ding YM, Wang B, Wang WX, et al. new classification of the anatomical variations of cystic artery during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13(42):5629-563.
- Ding YM, Wang B, Wang WX, et al. New classification of the anatomical variations of cystic artery during laparoscopic chole cystectomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13(42):5629-5634.
- Hollinshed WH. The Liver and Gall bladder. Anatomy for Surgeons. The Thorax Abdomen and Pelvis. vol. 2. New York: Harper and Brothers. 1956: 346-347.
- Jansirani D, Mugunthan N, Phalgunan V, et al. Caterpillar hump of right hepatic artery: incidence and surgical significance. Natl J Clin Anat. 2012; 1(3): 121-124.
- Michels NA. Blood Supply and Anatomy of the Upper Abdominal Organs with Descriptive Atlas. Philadelphia: Lippincott Company. 1955: 171-175.
- Hamza MU, Jaffar AA, Hassan HA, et al. Vascular and gall bladder variations in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Med J Babylon. 2008; 5(1): 119-130.
- Johnston EV, Anson BJ. Variations in the formation and vascular relationships of bile ducts. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1952; 94: 669-686.
- Kavitha B. An anatomical study of Moynihan’s hump of right hepatic artery and its surgical importance, J Anat Soc India. 2016.
- Bergamaschi R, Ignjatovic D. More than two structures in Calot’s triangle: a post-mortem study. Surg Endosc. 2000; 14: 354-357.
- Ayyaz M, Fatima T, Ahmed G. Arterial anatomy in Calot’s triangle as viewed through the laparoscope. Ann King Edward Med Coll. 2001; 7: 183-185.
- Al-Sayigh HA. The incidence of cystic artery variation during laparoscopic surgery. Med J Babylon. 2010; 7: 389-403.
- Mishall PL, Rajgopal L. Variant right hepatic artery forming Moynihan’s hump - clinical relevance. Int J Anat Var. 2010; 3:144-145.
- Bhargava GS, Singh H, Singh HD, et al. Moynihan’s hump of right hepatic artery: a case report and surgical significance. CIBTech J Surg. 2014; 3(2): 42-44.
- Bagadabettu SN, Sirasanagandha SR, Kumar N, et al. Hepatosplenic trunk associated with tortuous course of right hepatic artery forming caterpillar hump. N Am J Med Sci. 2012; 4: 376-378.
- Bulut T, Yamaner S, Bugra D, et al. False aneurysm of the hepatic artery after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Acta Chir Belg. 2002; 102: 459-463.
- Alves A, Farges O, Nicolet J, Watrin T, Sauvanet A, Belghiti J. Incidence and consequence of an hepatic artery injury in patients with post cholecystectomy bile duct strictures. Ann Surg 2003; 238: 93-96.
- Schmidt SC, Settmacher U, Langrehr JM, Neuhaus P: Management and outcome of patients with combined bile duct and hepatic arterial injuries after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surgery 2004; 135: 613-618.
- Halasz NA. Cholecystectomy and hepatic artery injury. Arch Surg. 1991; 126: 137-138.
- Chapman WC, Halevy A, Blumgart LH, Benjamin IS. Post-cholecystectomy bile duct strictures: management and outcome in 130 patients. Arch Surg. 1995; 130: 597-604.
- Deziel DJ, Millikan KW, Economou SG Doolas A, Ko ST, Airan MC: Complications of laparoscopic chomesystectomy: a national survey of 4,292 hospials and an analysis of 77,704 cases. Am J Surg. 1993; 165: 9-14.
- Bismuth H: How to treat a postoperative stenosis? in Bismuth H, Lazorthes F (eds): Operative Injury of the Common Bile Duct. Paris, Masson. 1981: 47-107.
- Nicholson T, Travis S, Ettles D, Dyet J, Sedman P, Wedgewood K, Royston C: Hepatic artery angiography and embolization for haemobilia following laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1999; 22: 20.
- Connor S, Garden OJ: Bile duct injury in the era of laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Br J Surg. 2006; 93: 158-168.
- Frilling A, Li J, Weber F, Frubauf NR, Engel J, Beckebaum S, et al. Major bile duct injuries after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a tertiary center experience. J Gastrointest Surg. 2004; 8: 679-685.
- Al-Sayigh HA. The incidence of cystic artery variation during laparoscopic surgery. Med J Babylon. 2010; 7:389-403.
- Mishall PL, Rajgopal L. Variant right hepatic artery forming Moynihan’s hump - clinical relevance. Int J Anat Var. 2010; 3:144-145)
- Jansirani D, Mugunthan N, Phalgunan V, et al. Caterpillar hump of right hepatic artery: incidence and surgical significance. Natl J Clin Anat. 2012; 1(3): 121-124.
- Bhargava GS, Singh H, Singh HD, et al. Moynihan’s hump of right hepatic artery: a case report and surgical significance. CIBTech J Surg. 2014; 3(2): 42-44.
- IKeith L. Moore, clinically oriented anatomy, 6th edition. 2009; 287-288.
- Hamza MU, Jaffar AA, Hassan HA, et al. Vascular and gall bladder variations in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Med J Babylon. 2008; 5(1): 119-130.
- Ding YM, Wang B, Wang WX, Wang P, Yan JS. New classification of the anatomic variations of cystic artery during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(42): 5629-34.
- Nagral S. Anatomy relevant to cholecystectomy. J Min Access Surg 2005; 1(2): 53-8.
- Tebala GD, Innocenti P, Ciani R , Zumbo A , Fonsi GB, Bellini P et al. Identification of gallbladder pedicle anatomy during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Chir Ital. 2004; 56(3): 389-926(1): 75-6.
- Suzuki M , Akaishi S, Rikiyama T, Naitoh T, Rahman MM, Matsuno S. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy, Calot’s triangle, and variations in cystic arterial supply. Surg Endosc. 2000; 14: 141-4.
- Ignjatovic D, Zivanovic V, Vasic G, Kovacevic-McilwaineI. Cystic artery anatomy characteristics in minimally invasive surgical procedures. Acta Chir Iugosl. 2006; 53(1): 63-6.
- Balija M, Huis M, Nikolic V, Stulhofer M. Laparoscopic visualization of the cystic artery anatomy. World J Surg. 1999; 23: 703-7
- Hugh TB, Kelly MD, Li B. Laparoscopic anatomy of the cystic artery. Am J Surg. 1992; 163(6): 593-5.

