Clinical Image - Volume 3 - Issue 3
A rare tumor of atypical scrotal location
Kenza Tahri Joutei Hassani*; Zakia Douhi; Hafsa Hamraoui; Hanane Baybay; Sara Elloudi; Meryem Soughi; Fatima Zahra Mernissi
Department of Dermatology, University Hospital Hassan II, Morocco.
Received Date : April 14, 2023
Accepted Date : May 19, 2023
Published Date: May 26, 2023
Copyright:© Tahri Joutei Hassani Kenza 2023
*Corresponding Author : Tahri Joutei Hassani Kenza, Department of Dermatology, University Hospital Hassan II, Fes, Morocco.
Email: kenzatahri10@gmail.com
DOI: Doi.org/10.55920/2771-019X/1447
Abstract
Apocrine hidrocystoma is a rare benign adnexal tumor considered a cystic proliferation of the apocrine glands, rather than simple retentive cysts of the apocrine sweat glands [3]. It occurs most often in adults on the neck and head and especially on the external canthus of the eye [1,2]. They vary in size from 3 to 15 millimeters and are most often pigmented, blue, blue-black, grayish, translucent or violet in color. Apocrine hidrocystomas located in other sites such as the shoulders, fingers, abdomen and genital region have been rarely described.Differential diagnoses of apocrine hidrocystomas of scrotal location include eccrine hidrocystomas, blue nevus, melanoma, median raphe cyst, milium grain, epidermoid or pilar cyst, and hemolymphangioma [1,2].
The treatment of these lesions is surgical excision without margin when they are single lesions. Other methods that have shown good results include carbon dioxide vaporization and laser treatment [4].
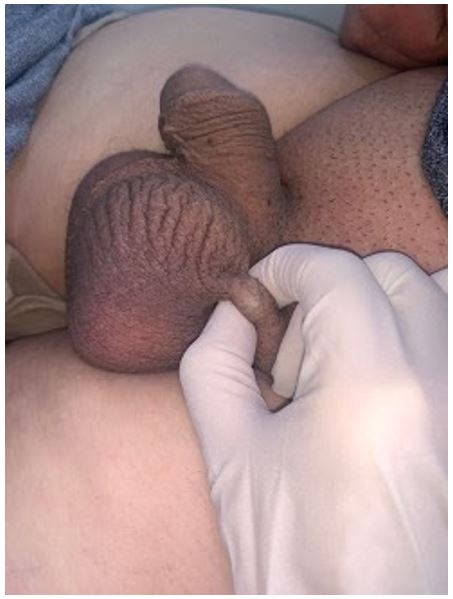
A 45-year-old man with no notable pathological history presented to our department with a left scrotal subcutaneous formation that had been progressively evolving for 1 year.The clinical examination found a subcutaneous nodule of cystic consistency measuring approximately 1 cm. It was not tender, the skin covering the cyst was normal. There was no evidence of pain, tenderness, pruritus, or other symptoms.A scrotal ultrasound was ordered.
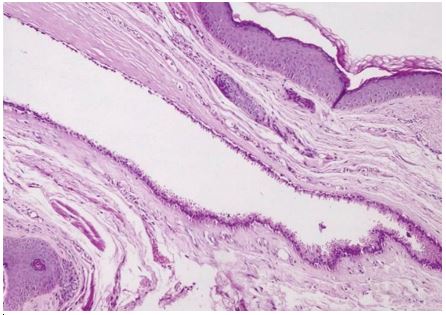
Excision of the mass was performed under local anesthesia.Histological examination noted the presence of a cystic formation bordered by a double layer of secretory columnar cells with decapitation images.the peripheral cubic layer was made of myoepithelial cells. There were papillary projections within the cavity.The diagnosis of scrotal apocrine hidrocystoma was made.
Figure 1: Clinical image : subcutaneous scrotal nodule.
Figure 2: A cystic cavity occupying the dermis made of a double cell layer; one external lined with vacuolated myoepithelial cells and the other internal lined with columnar cells with eosinophilic secretory cytoplasm (Hematoxylin Eosin, magnification x10).
References
- Matsuyama T, Yahagi E, Mabuchi T. Apocrine hidrocystoma on the genitalia of a 9-year-old girl. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018; 35: e231-4.
- Samplaski M, Somani N, Palmer J. Apocrine hidrocystoma on glans penis of a child. Urology 2009; 73: 800-1.
- Park J, Kim I, Jang HC, Park K, Kim Y, Chung H. Linear skin- coloured papules on scrotum: a quiz. Acta Derm Venereol. 2015; 95: 762-5.
- Sarabi K, Khachemoune A. Hidrocystomas - A brief review. Med Gen Med 2006; 8: 57.