Research article - Volume 4 - Issue 2
Navigating the Path to Student Retention: Exploring the impact of mentorship, preceptors, and clinical readiness
Kelli D Whittington1*, Jonathan Montoya2
1School of Health Sciences, Southern Illinois University Carbondale, Carbondale, Illinois, USA.
2BSN senior student at Southern Illinois University Carbondale, Carbondale, IL, USA.
Received Date : Feb 06, 2024
Accepted Date : Mar 04, 2024
Published Date: Mar 11, 2024
Copyright: © Whittington KD 2024
*Corresponding Author : Kelli D Whittington School of Health Sciences, Southern Illinois University Carbondale, Carbondale, Illinois, USA.
Email: kellid@siu.edu
DOI: Doi.org/10.55920/2771-019X/1645
Abstract
This study further investigates the crucial factors that influence student retention rates, focusing on the impact of mentorship, preceptors, and clinical readiness. With the growing concern regarding student retention rates in higher education institutions, it is important to identify effective strategies that help enhance the retention rates. The study will adopt a mixed methods approach using quantitative and qualitative data combining survey and preceptor evaluations to gain insight into students' experiences and perceptions while in a Bachelor of Science in Nursing program at a public university in the mid-west. All data collected examined how various factors influence student retention while focusing on mentorship, preceptorship, and clinical readiness, improving student success rates and graduation rates. The findings also provide a catalyst for positive change, driving the selected BSN program to improve preceptorship opportunities, strengthen clinical readiness and provide various mentoring opportunities. It is also important to note what strategies have been effective for the program and continue implementing them to future cohorts. In conclusion, this research will contribute to the ongoing topic on student retention, offering valuable insights received from the study.
Introduction
Student retention is vitally important within nursing institutions, shaping the trajectory of future healthcare professionals. Identifying and understanding factors that significantly influence student retention rates hold importance for nursing education programs, allowing them to refine their educational practices and ensuring the continued success of their students. In this context, the current literature review explores existing research surrounding student retention, with a focus on a Bachelor of Science in Nursing program. Nursing education programs must recognize the significance of fostering an environment that supports students' academic and professional growth. As students start their journey into the nursing profession, it is important to comprehend the several components contribute to their profession and commitment. Among these influential factors, mentorship, preceptors, and clinical readiness are key determinants that impact students’ retention and performance during their time in the nursing program. The primary objective of this literature review is to synthesize the extant research on student retention, by examining the impact of mentorship, preceptors, and clinical readiness, this study aims to shed light on critical areas of improvement for the nursing education program, fostering the development of robust support mechanisms and enhancing the overall educational delivery.
Statement of the problem: As a higher education institution, it is important to recognize student retention in the nursing program. As nursing programs strive to create a supportive learning environment, it is important to identify and address underlying issues that hinder student success rates and impede student success in their educational journey. This study examines student retention rates and compares them with insights from the student, preceptors, and mentors. By using the experiences, the study will provide insights to improve the nursing program and create an improved learning environment.
Objectives:
- Identify the key factors influencing student retention rates within a nursing program.
- Examine the impact of mentorship on nursing students' retention and academic success.
- Explore the role of preceptors in shaping nursing students' perceptions and their correlation with their commitment to the profession.
- Assess the significance of clinical readiness in influencing nursing students' persistence in their educational journey.
Literature Review: Student retention is an important aspect for nursing institutions. Understanding the factors that influence student retention is important for education programs to improve their education practices and ensure the success of students. This literature review will explore the existing research on student retention by examining factors such as mentoring, preceptors, and clinical readiness. Identifying and understanding these factors will provide an insight for nursing education programs to develop good support mechanisms, enhance their educational delivery program and improve their student retention rates.
Mentoring: Mentoring plays a significant role in the professional development of nursing students and can positively impact the success of a student. The purpose of mentoring is to facilitate growth, development, and success of the mentee [1]. Mentoring goes beyond simple teaching or instruction; it involves fostering a supportive and nurturing relationship where the mentor can provide guidance, advice, and feedback towards the mentee’s goals. It makes learning easier and by expressing latest ideas or thoughts about a situation.
Peer mentors present themselves as resources for nursing student mentees at the secondary appraisal stage [2]. The secondary appraisal stage is evaluating resources available to overcome a stressor. Peer mentors provide both problem-focused and emotion-focused support through their lived experiences and survival tips in becoming a nurse. The frequency and quality of the mentor-mentee seems more critical than the program's duration. Mentors can influence the overall well-being, confidence, and success of nursing students. Sharing their own personal experiences develops a sense of resilience and growth to prepare for their nursing profession. Today’s workforce would rather connect with experts and fellow workers in a collaborative, intentional learning process than search for answers in impersonal databases or random contacts in social networking sites [3]. This intentional learning engagement allows people to learn through the lived experiences of others rather than other non-personal sources. Being able to connect with others makes learning easier and allows the learner to correlate an existing experience with their own given situation. Also of importance is the expanding of personal views and thinking on the concepts of group mentoring. Group mentoring should be viewed as topical learning that occurs in a peer environment. This will help set the right expectations for learners, advisors, and program administrators alike, creating endless opportunities for open, ongoing learning. Creating an optimal learning environment between the mentee and the mentor is essential to the promotion of student retention, ensuring a strong educational connection.
Preceptors: Student retention is important for nursing programs and the quality of future healthcare professionals. Preceptors are experienced nurses who provide guidance and support to students, primarily during clinical learning opportunities, where they play a vital role in shaping a student's education and career by demonstrating role professionalism. Existing research provides insight on preceptors and how they prepare students at clinical sites. Also noted are how preceptors influence students to find a sense of belonging in the nursing program. Preceptors agreed that to be effective preceptors, it was important to know ways to help students learn, have knowledge of course and evaluation requirements, and know how to interact with students [4]. To help students learn, preceptors emphasized the need to know the students' goals and objectives early in the experience, and how to foster development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Preceptors need a thorough understanding of the evaluation process including how to use the evaluation forms provided by the university and how to decide whether students were meeting course objectives (passing or failing). Preceptors also agreed it was important to understand principles of adult learning and adult learning styles. It is necessary to reorganize the preceptor education program so that preceptor nurses receive a high level of mentoring [5]. Rather than only focusing on basic nursing practice, current preceptor education programs should be innovative and include an in-depth education program designed to improve career, psychosocial and role modeling functions among the identified mentoring functions. This allows preceptors to be prepared to best practice role modeling to novice nurses in a positive way that implicates their practice. Having prepared preceptors that are helping nursing students will reflect and help with student retention. The function of preceptors in their mentoring role, as perceived by novice nurses, affected their self-efficacy and organizational commitment.
Clinical Readiness: Workplace readiness is a critical aspect of the transition from student to professional nurse, as it ensures that newly qualified nurses are ready to supply the healthcare environment's demands. This readiness demonstrates the skills, knowledge, and support necessary for nurses to provide safe and effective care and be competent caregivers. Workplace readiness is relevant as healthcare faces challenges in new graduate nurses overcoming the gap between nursing education and clinical practice. By analyzing preceptor clinical evaluations sheets, this review will demonstrate factors influencing workplace readiness, challenges by newly qualified nurses, and strategies to prepare them for professional practice. Mentorship and preceptorship programs facilitated workplace readiness. Managers, educators, and preceptors shared the role they play in supporting newly graduated nurses, ensuring they receive support during the new shift from student to healthcare professional (Grayem, K., 2019). When students are not adequately prepared when they enter the workforce, it can place a risk to patient safety, jeopardize the quality of care, and retention of nursing [6]. Newly graduated nurses are often expected to apply all information learned straight into practice after graduation this can be an area of concern when nurses are still developing clinical competence. Preceptors may believe new nurses need more assistance but are more likely to be successful in their new carrier regardless of experience due to there not being an expectation for readiness as a new nurse [7]. This makes RN graduates feel more prepared in their clinical practice due to the presence of experienced mentors and preceptors. Additionally, the importance of organizational support and alignment between nursing education and the clinical practice environment is noted. Managers and educators expressed that supportive environments foster collaboration, teamwork, and a positive learning environment.
Methodology: This study uses a mixed methods approach, involving both quantitative and qualitative research aspects. The qualitative approach allowed for the collection of student responses via a survey about the mentoring opportunities they have experienced while in the nursing program. The quantitative aspect was obtained from evaluations sheets completed by preceptors measuring the students' clinical readiness. The combination of these methods allows for an exploration of the impact of mentorship, preceptors, and clinical readiness with student retention in a particular nursing program.
Data Collection and Participants: The university’s intuitional board approved this study. Once consent was obtained, data was collected from students enrolled in a BSN nursing program for the 2022-2023 academic year. Recruit subjects were contacted via classroom announcement within the university learning management system, with all responses retaining anonymity.
Results
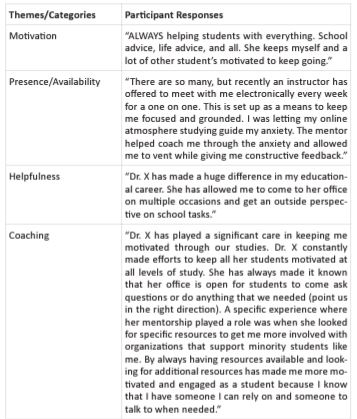
To quantitatively assess the impact of mentoring/preceptorship, students were asked to share a specific experience or story where mentorship played a significant role in keeping the student motivated and engaged in their nursing studies. The responses were grouped according to theme, with the following four themes being identified: motivation, presence/availability, helpfulness, and coaching. Specific examples of the student responses related to each theme is shared in Table 1.
The theme for motivation emerged prominently from participants' responses regarding their experiences with mentors. Mentors were mentioned as significant sources of motivation for some individuals within the nursing program. Participants expressed that mentor’s played a vital role enhancing their personal motivation. Respondents mentioned specific instances where their mentor provided encouragement and assistance in challenging times.
Presence/Availability: Participants frequently highlighted the importance of a mentor's presence and availability in their personal and professional development. The availability of mentors to listen and offer guidance was viewed as a crucial factor in establishing a trusting and supportive relationship. Respondents mentioned that mentors who made themselves accessible have benefited the student’s academic progression by keeping them focused with their education.
Helpfulness: The helpfulness of mentors was a consistent theme identified in the received responses. Participants acknowledged that mentors not only offered guidance but also actively contributed to problem solving. They often provided valuable insights and constructive feedback to enhance the mentees' understanding of their individual approaches and what could be done to improve and enhance those approaches. The willingness of mentors to share their knowledge and experiences is a key factor in facilitating mentees' growth and learning.
Coaching: The final theme that emerged from the qualitative data was the mentor's role as a coach. Participants emphasized that mentors not only offered guidance but also actively supported their mentees' efforts and celebrated their achievements. The mentors' coaching even touched some students by encouraging their active engagement within campus organizations. Student’s reported this promotion of student engagement also positively impacted their performance in their academic studies.
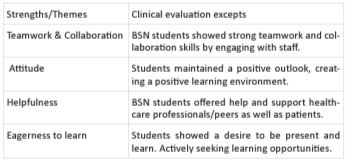
Preceptors: Qualitative and quantitative data was examined from 302 clinical evaluations from juniors, seniors, and accelerated students to determine consistent themes noted by both self-reflection required of the student and the clinical faculty evaluating BSN student performance. Clinical evaluations are used in every clinical course to foster clinical readiness across the curriculum. Identified strengths include the students' teamwork, collaboration, attitude, helpfulness, and eagerness to learn. Nurturing these strengths across courses positively impacts student retention, while developing a path of success for students as future healthcare professionals. By developing these strengths throughout a student academic journey, a foundation is provided to ensure the student enters the workforce with enhanced performance to meet the challenges that the healthcare industry brings.
Clinical readiness: Clinical readiness was evaluated by quantifying the students’ display of a positive attitude and ability to interact utilizing professional communication with staff and patients. Nurse preceptors completing the preceptor evaluation ranked their student on a Likert scale where 1 = strongly disagree and 5 = strongly agree and provided an average of 4.9, demonstrating BSN nursing students in the preceptor-led clinical setting consistently displayed a positive attitude and utilized professional communication with both staff and patients. Also evaluated was the ability of the student to seek out learning opportunities. Using the same Likert scale, Nurse preceptors completing the preceptor evaluation provided an average of 4.88, demonstrating BSN nursing students in the preceptor-led clinical setting consistently sought out learning opportunities with an eager attitude. The ability of the student to accept constructive feedback and develop a plan of action for improvement was also measured. An average of 4.91 was obtained when nurse preceptors completing the evaluations on this aspect, demonstrating BSN nursing students in the preceptor-led clinical setting consistently accepted constructive feedback in a way that promoted action for improvement. Qualitative data identified the following themes: students were eager to learn, helpful, professional and a team player. The themes that were identified are beneficial for students once they arrive at the clinical setting. These qualities help their learning experiences and boost their quality of patient care. Feedback benefits students by helping them grow as healthcare professionals.
Table 1: Qualitative themes and response examples.
Table 2: Quantitative scores for Qualitative themes.
Table 3: Preceptor themes on student performance.
Preceptors evaluation themes: Qualitative data was extracted from over 300 clinical evaluations completed by preceptors. Identified strengths include the students' teamwork, collaboration, attitude, helpfulness, and eagerness to learn. These strengths, necessary in the workforce, also positively impact the ability of the nursing student to persist in the BSN program. Identified themes found recurring across the majority of successful clinical evaluations (successful evaluation is noted to have a passing score in the course) included teamwork and collaboration, attitude, helpfulness and an eagerness to learn.
Discussion
This study investigated the impact of mentorship, preceptors, and clinical readiness on student retention. Participants emphasized the significant role mentors play in keeping students motivated throughout their academic careers. Mentors demonstrated a commitment that went beyond academics, fostering total personal and professional development, going beyond typical advising and looking for resources to support students' success in the program. The developing impact of mentorship in educational settings is highlighted by these findings. The mentoring relationship goes beyond only providing advice and turns into a tool of development. Based on the quantitative study of preceptor assessments, BSN nursing students excel at teamwork, positive attitude, helpfulness, and eagerness to learn. These characteristics demonstrate the consistency between mentorship experiences and clinical performance and are consistent with the themes found in the qualitative analysis. The combination of these results points to a mutually beneficial relationship between clinical readiness and mentoring. Mentoring improves students' character traits, which aids in their success in clinical settings. This demonstrates how mentoring initiatives can help to develop nurses that are highly motivated in their career and to deliver the highest quality care to patients. Although this research offers insightful data, it is important to recognize its limits in terms of sample size, context and lack of validated survey instrument. Targeted mentoring interventions and their long-term benefits on student outcomes could be the subject of a further examination.
Conclusion
In summary, this study provides more light on the significant influence that mentoring has on students' motivation and the growth of clinical readiness attributes. The interaction between mentors, students, and their readiness for the healthcare profession is portrayed in detail through the integration of qualitative and quantitative data. Nursing education can further improve student achievement and the standard of patient care by recognizing and utilizing the possibilities of mentoring, preceptors, and clinical readiness
References
- Smirti. Which of the following statements best exemplifies the importance of mentoring?. Management Notes. 2023. https://www.managementnote.com/which-of-the-following-statements-best-exemplifies-the-importance-of-mentoring/.
- Lim S, Lim X M, Wen C C J, Dong C Y, Mikkonen K & Wentao Z. Peer mentoring programs for nursing students: A mixed methods systematic review. Nurse Education Today. 2022; 105577.
- Emelo R. Group mentoring best practices. Industrial and Commercial Training. 2011; 43(4): 221-227.
- Gubrud P. Teaching in the clinical setting. In D.M. Billings & J.A. Halstead (Eds.), Teaching in nursing: A guide for faculty (5th ed.) Elsevier. 2016.
- Choi E & Yu S. Effects of preceptors’ mentoring function on novice nurses’ self-efficacy and organizational commitment: A cross-sectional study. Nurse Education in Practice. 2022; 64: 103431.
- Rusch L, Manz J, Hercinger M, Oertwich A, McCafferty K. Nurse preceptor perceptions of nursing student progress toward readiness for practice. Nurse Educator. 2029; 44(1): 34-37. DOI: 10.1097/NNE.0000000000000546
- Robinson C. Are nurse preceptors the new clinical instructors? MedSurg Nursing. 2022; 31(1): 55-56.